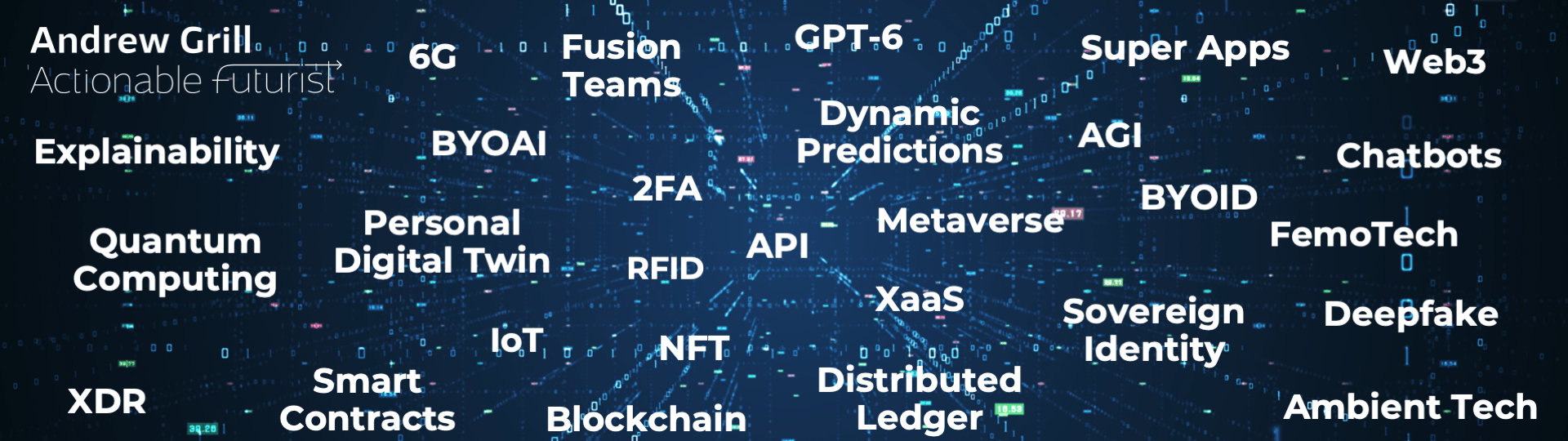
In all of my presentations, I show a slide designed to scare my audience into action. I call it the “scary slide”. It is full of jargon and acronyms and I challenge my audience to find out what all these terms mean as they will soon impact their business.
Look for the full scary slide at the end of this video. How many of these could you say you understand?
Here is an explanation of each of the terms on this slide
- 6G: The next generation of wireless communication technology expected to offer faster speeds and more reliable connections than 5G.
- Fusion Teams: Cross-functional teams that integrate various disciplines to foster innovation and agility within organisations.
- GPT-6: The anticipated sixth generation of the Generative Pre-trained Transformer model, likely to feature more advanced natural language processing capabilities.
- Super Apps: Multi-functional apps that integrate various services such as messaging, payments, and shopping into one platform.
- Web3: The third generation of the World Wide Web focused on decentralisation and blockchain technologies.
- Explainability: The ability to describe how AI and machine learning models make decisions in a way that is understandable to humans.
- BYOAI (Bring Your Own AI): A trend where individuals or organisations can use their own artificial intelligence models or systems within larger frameworks.
- 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication): An additional layer of security used to ensure that people trying to gain access to an online account are who they say they are.
- Dynamic Predictions: The use of real-time data and advanced algorithms to make forecasts that can adjust and improve continuously.
- AGI (Artificial General Intelligence): A level of artificial intelligence where machines possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks as humans do.
- Personal Digital Twin: A virtual replica of an individual that mirrors their characteristics, behaviours, and decisions using data and simulations.
- RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification): A technology that uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects.
- API (Application Programming Interface): A set of protocols and tools for building and interacting with software applications.
- Metaverse: A collective virtual shared space, created by the convergence of virtually enhanced physical reality and physically persistent virtual reality.
- XaaS (Anything as a Service): A collective term referring to the delivery of various services and applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
- Sovereign Identity: A digital identity that is owned and controlled by the individual rather than any centralised authority.
- Quantum Computing: An area of computing focused on developing computer technology based on the principles of quantum theory.
- Deepfake: Synthetic media where a person in an existing image or video is replaced with someone else’s likeness using artificial intelligence.
- IoT (Internet of Things): The network of physical objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet.
- NFT (Non-Fungible Token): A unique digital asset that represents ownership or proof of authenticity of a particular item, typically used for digital art and collectibles.
- Distributed Ledger: A digital system for recording the transaction of assets in which the transactions and their details are recorded in multiple places at the same time.
- Blockchain: A type of distributed ledger technology that uses a chain of blocks to record transactions securely, transparently, and immutably.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code.
- Chatbots: Computer programs designed to simulate conversation with human users, especially over the internet.
- FemoTech: Short for Femtotechnology – a theoretical field of technology that involves the manipulation of matter at the scale of femtometres, or one quadrillionth of a metre, focusing on the manipulation of atomic nuclei and subatomic particles.
- XDR (Extended Detection and Response): A cybersecurity approach that integrates multiple security products into a cohesive system to provide comprehensive threat detection and response.
- Ambient Tech: Technology that is integrated seamlessly into the environment, providing services and information without requiring active user interaction.